Do Blue Jays Migrate? Migratory Patterns And Factors Affecting

Blue Jays are a common sight in North America, but do they migrate? The answer is not as simple as it seems, some Blue Jays migrate whereas others do not.
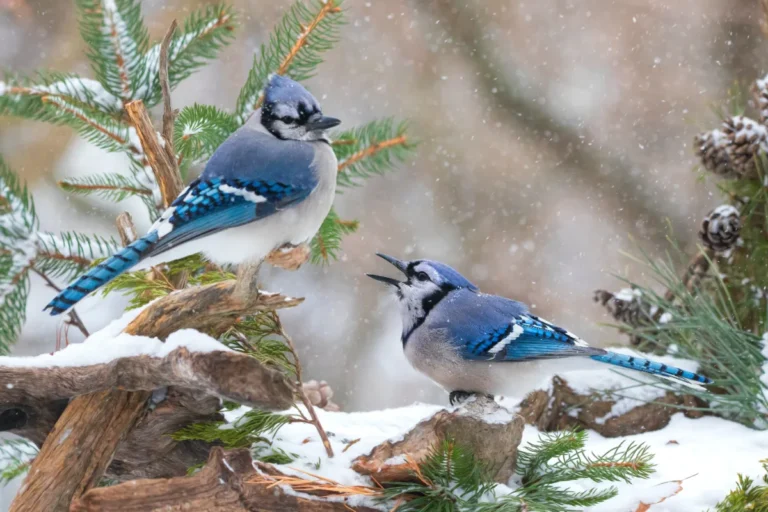
Before getting into the topic, Do Blue Jays Migrate? Let’s get familiar with these species. Blue Jays are a popular bird species. It is a loud and colorful bird commonly found in eastern backyards and woodlands.
They are easy to recognize because of their distinctive appearance. These birds are smart and can adapt to different food sources. Apart from their loud “jay! jay!” calls, they can produce various musical sounds.
In this blog post, we will explore the interesting topic of Blue Jays and their migration habits in more detail. So, stick with us till the end.
Migratory Behavior
Breeding jays may be migratory in one year, sedentary in the next, and migratory again in a subsequent year. This irregularity raises questions about the factors influencing their decision. Blue Jays’ migratory behavior remains mysterious due to their;
- Unpredictable patterns
- Varying migration distances
- Potential food-driven migration
- Regional differences
Understanding Migration
Bird migration and its significance
Birds migrate from areas of low or decreasing resources to areas of high or increasing resources. As it is a vital aspect of the avian lifespan.
Read More: How To Get Rid Of Blue Jays In Your Yard? | 6 Natural Ways>>>
Likewise, it allows birds to move from places with little or diminishing resources. They have plenty of growing resources, like food and places to build nests. Migration also plays a vital role in the distribution of genes and their maintenance.
Reasons Why Birds Migrate
The complete reasons behind bird migration remain unclear. However, it is thought that the amount of food, the chances of having babies, and the weather all have a big impact.
Birds move to places where there is plenty of food and fewer other birds compete for places to build nests.
As temperatures drop and food becomes scarce, birds move to warmer regions. It is where food and nesting opportunities are more abundant.
Common Patterns And Routes of Migration
Birds usually migrate in specific directions, often from north to south. During their migration, they make stops to rest and refuel.
Similarly, these migration routes can change as the weather and climate change. When this happens, birds must adjust their paths accordingly.
However, some birds need to travel incredibly long distances, spanning thousands of miles, to reach their destination.
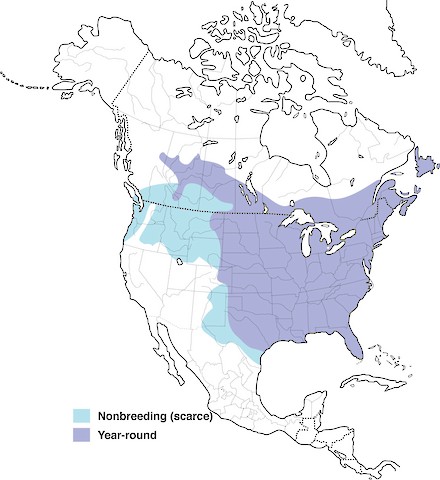
Blue Jays: Resident or Migrant?
Blue Jays come in two groups. Some live in one place all year, while others move to different places at certain times.
Resident Blue Jays
Some Blue Jays stay in one place all year long and don’t migrate. These Jays usually live longer as they don’t have to go through the tough journey of migration.
Further, they can handle cold winters in their home areas, although some choose to stay where they were born instead of moving around.
Resident Populations and their year-round presence
Resident populations of Blue Jays are those that remain in their breeding range year-round.
- Resident Blue Jays tend to live longer than migratory Blue Jays. The migratory journey can be The activity is physically demanding for the birds themselves.
- Some Blue Jays are year-round residents and do not migrate. For example, the Blue Jay populations in Texas appear to be resident year-round.
- They can survive the winter in colder climates. And some may choose to remain in their breeding range rather than migrate.
Overall, resident Blue Jays are those that remain in their breeding range year-round.
Migratory Blue Jays
Some Blue Jays move from one place to another in search of food. Moreover, lots of blue Jays do this every year, and they might travel in big groups with thousands of other Jays.
Migratory populations of Blue Jays undertake seasonal movements in response to environmental factors. Here are three points highlighting the migratory populations and their seasonal movements.
Migratory patterns
Blue Jays exhibit two general migration patterns. Some individuals are usually present year-round, while others migrate seasonally. The species is partially migratory, and only some Blue Jays migrate each year. Those that migrate may travel in flocks consisting of thousands of individuals.
Migration routes
Blue Jays usually follow set migration paths called flyways. They are north-south routes offering places to rest and refuel.
However, these routes can change due to climate change. It causes the birds to adjust their paths. As it makes them longer or shorter, or even abandoning them entirely.
Reasons for migration
Blue Jays may migrate in response to environmental factors such as food availability. When temperatures decrease and food becomes scarce, Blue Jays migrate to warmer areas. It is where food and nesting opportunities are more abundant.
Factors Influencing Blue Jay Migration
The factors influencing Blue Jay migration are complex. It may vary among individuals and populations. They are known to migrate in response to food availability.
When it gets colder and food becomes scarce where they usually breed, they might go to warmer places. It is where food and nesting opportunities are more abundant.
The presence of acorns, nuts, seeds, and other food may influence their migration patterns. Besides that, the various factors that influence the migration patterns of Blue Jays include.
- Climate and Temperature
- Food availability
- Breeding opportunities
Environmental factors affecting migration
Blue Jay migration faces several challenges. Some of them include food availability and climate change.
Food availability
Food is one of the main reasons for bird migration. Their travel is linked directly to the availability of vegetation. Blue Jays may migrate in response to food availability, as they move to areas where food is more abundant. Food availability may affect migratory behavior.
Weather conditions
Weather patterns and climatic conditions may also influence Blue Jay migration. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and other environmental cues may trigger their migratory behavior. Climate extremes impact poor and vulnerable communities immediately and persistently. It leads to increased risks of food shortages. It can further fuel internal and external migration.
Role of photoperiod (day length) in triggering migration
Photoperiod, or day length, is a crucial environmental key. It influences the timing of bird migration, including Blue Jays. Photoperiod manipulation can impact bird migration timing.
However, other environmental cues may also play a role. Further research is needed to fully understand these factors and mechanisms.
Migration patterns And Routes followed by Blue Jays
Blue Jays display partially migratory behavior. Some individuals migrate, while others stay in their breeding range. They follow established flyways and may travel in loose flocks during the day.
As climates change, bird migration routes are not fixed. It can either become longer or shorter, or birds may stop using them entirely.
Geographic or Genetic FactorsInfluencing Migration Patterns.
Blue Jays from the north tend to migrate more than those from the south. Genetic factors may also play a role in Blue Jay migration.
But we don’t completely understand which genes or how they work.
Additionally, if there are good places to stop and rest, their journey can also impact how Blue Jays decide to migrate.
Research and Findings
Scientific studies and Research on Blue Jay migration
Research has shown that some Blue Jays will migrate south for some years. Meanwhile, others will remain in their breeding range.
Blue Jays are partially migratory, and only some individuals migrate each year. Age is believed to play a role in the migration patterns of Blue Jays. Most migrating birds are believed to be young.
A study was conducted in the North American Bird Bander to track Blue Jays. The birds were banded in the fall season in the northeastern United States. They were recovered in the winter in the southeastern United States.
Tracking Methods and Technologies used to study their movements
Technologies used to study blue jay’s movements are;
- GPS (Global Positioning System) Tags
- Radio Transmitters
- Satellite Telemetry
- Geolocators
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) Tags
Further, Scientists use a variety of methods to track bird movements. It includes banding and recapture, radio tracking, and network analysis.
Radio Tracking
It allows real-time tracking of a bird’s movements. It uses a small radio transmitter.
Banding and Recapture
Banding helps researchers follow a bird’s movements and survival. It is by attaching a small band to its leg.
Network Analysis
Network analysis involves studying the social interactions and movements of blue jays within their flock or community.
Some Interesting discoveries or insights from migration studies.
- Blue Jays migrate during the day, unlike most songbirds that migrate at night.
- Blue Jays often gather in flocks, particularly during migration.
- They are recognized by their steady flight with rounded wings and long tails.
Migration Strategies of Blue Jays
Strategies used by Blue Jays during migration.
The strategies used by Blue Jays during migration are:
- Visual Landmarks: Blue Jays depend on optical signals like rivers and mountains for finding direction.
- Sun Compass: Blue Jays use the sun’s position as a compass during the day.
- Magnetic Sensing: They detect the Earth’s magnetic field for routing, especially in cloudy conditions.
Stopover sites and their importance
Stopover sites are important rest areas for migrating Blue Jays. These places provide them with food, rest, and safety from dangers like predators.
Further, these sites are also helpful for them to stay on the right track during their migration. Also, these stopovers help them to find their way.
Leapfrog migration observed in Blue Jays
The Leapfrog migration of Blue Jays is like a big bird race. Some Blue Jays go really far, north or south during their trip, while others don’t go so far.
This means, the traveling Blue Jays end up passing over the ones who don’t fly as far. They do this because they want to find better places to eat and make their homes. It’s kind of like a game of tag in the sky!
Variations and Individual Differences
Mixed Migration Behavior
Blue Jays don’t all behave the same way when it comes to migration. Some decide to migrate, while others choose to stay where they were born.
Partial Migration
Blue jays are what we call ‘partially migratory’. This means that not all Blue Jays migrate each year. Some do, and some don’t.
Regional Differences
Blue Jays from the northern region tend to be more migratory. In contrast, Blue Jays from the southern region are more inclined to stay where they are.
FAQs
Do Blue Jays migrate?
Blue Jays typically migrate in the spring, from April to June.
What does a Blue Jays eat?
Blue Jays eat a variety of foods, like wild fruits, acorns, hazelnuts, etc.
What is the one interesting fact about the Blue Jays?
Blue Jays are known for their bright blue feathers and loud, piercing calls.






