Why Do Woodpeckers Peck Wood? 3 Fascinating Reason

Have you ever heard of or seen the woodpecker drilling a tree? If yes, then you might have wondered and asked yourself a question about it.
After all, it is a strange activity to peak woods even for the birds.
Woodpeckers are very mesmerizing birds. They have a unique habit of pecking wood which may seem unusual to many of us.
However, it is an essential and vital part of their survival.
Although it may appear that woodpeckers are causing harm to trees by pecking at them, this behaviour is actually crucial for their survival.
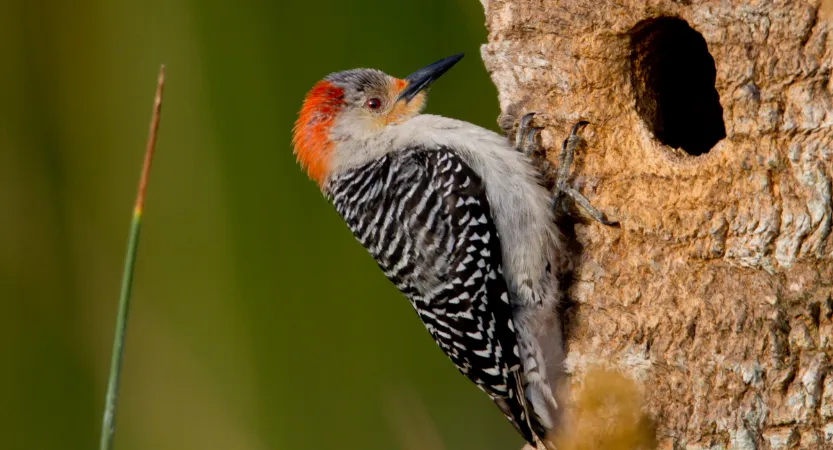

In this article, we will explore the reasons behind Why do woodpeckers peck wood? And, the anatomy that allows them to do it, and how it contributes to their survival.
Woodpeckers’ wood pecking behaviour is an essential part of their biology, allowing them to find food and create nesting cavities. Despite the intense impact of their pecking, woodpeckers have adapted well to avoid brain injuries.
Why Do Woodpeckers Peck Wood?
Woodpeckers are known for their unique behaviour of pecking wood. But why do they do it? Here are some reasons:
Finding Food
One of the primary reasons woodpeckers peck wood is to find food. Woodpeckers peck wood mainly to search for food. They have a varied diet that includes insects, nuts, and fruits.
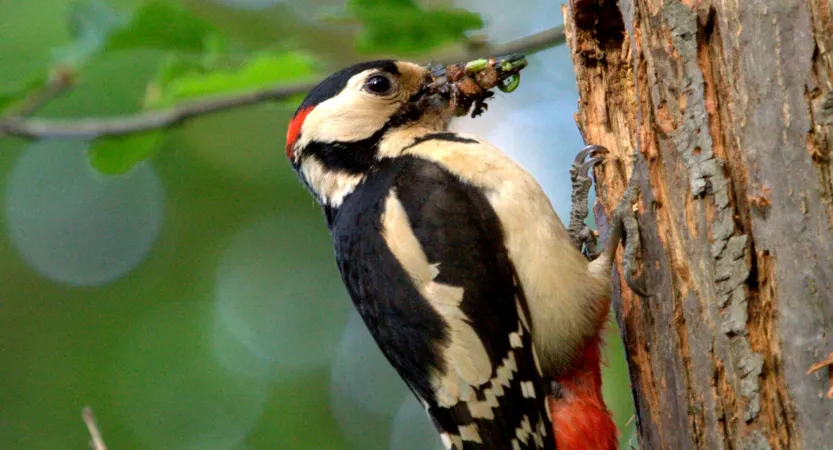

By pecking on trees, they can access insects hidden under the bark. When they find a potential meal, they use their specialized, barbed tongues to extract it from the tree.
Creating a Home
Another reason why woodpeckers peck wood is to create cavities for nesting purposes. Woodpeckers make their homes in tree cavities.
Once the cavities are ready, they add soft materials such as grass, feathers, or moss to make a comfortable place for their eggs to hatch. These cavities serve as homes for breeding pairs or roosting sites for individual birds during harsh weather conditions like winter months.
In addition, some species such as red cockerel also use nest holes made by other bird species such as mountain bluebirds which reduces the energy consumption required for creating new ones from scratch thus making it a more efficient way of nesting instead of starting all over again.
Communicating with Other Birds
Woodpeckers also peck on wood to communicate with other birds.
Woodpecker drumming is another form of communication between individuals belonging to the same species. They use their beaks to drum on hollow trees, producing a loud noise that can be heard by other woodpeckers.
They use different rhythms and frequencies depending on what message needs to be delivered
This behaviour is especially prevalent during mating season when they use the noise to attract a mate.
Additionally, woodpeckers use this method to mark their territory and let other birds know about potential sources of food.
For instance, male pileated woodpecker uses loud hammering sound against the wood to establish a territory which is heard from miles away.
Biology of Woodpeckers
Woodpeckers belong to the family Picidae and are found in many parts of the world. Woodpeckers have been around for millions of years, and they have evolved some unique adaptations to their environment.
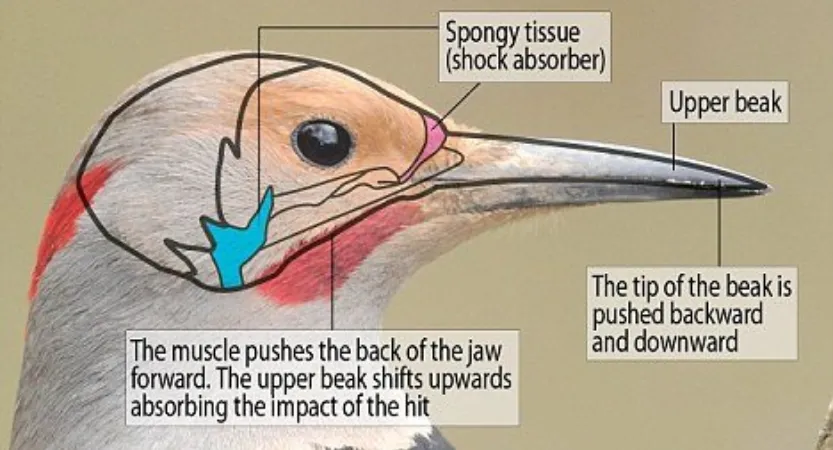
Woodpeckers have unique adaptations that enable them to peck wood with such force without injuring themselves.
Their skulls are thick and spongy, acting like a cushion to absorb the impact of their bill hitting the wood at high speeds. In addition, they also have a specialized muscle called “hyoid,” which wraps around their skull and acts as a shock absorber during pecking movements.
Woodpeckers also have barbed tongues that they use to extract insects from the wood and stiff tail feathers that help them brace against the tree trunk.
How Woodpeckers Avoid Brain Damage
Despite the forceful pecking, it’s impressive that woodpeckers don’t experience brain damage from the impact. But, their specialized anatomy allows them to avoid any harm.
Despite the protective adaptations, repeated pecking can still cause damage to the brain. To avoid this, the woodpecker has a built-in mechanism that helps maintain blood flow in its head while drilling holes into trees or branches. It involves the special arrangement of arteries and veins transporting blood through carotid artery instead if jugular vein in order to increase efficiency by reducing pressure on the skull thus preventing injury .
Source: Quora.com
The hyoid bone is an unusual bone that’s not found in other birds, and it’s located in the tongue, jaw and trachea. Another adaptation is a specialized brain structure that allows the woodpecker to adjust its head position to reduce the risk of injury.
Benefits of Pecking Wood
Woodpeckers’ pecking behaviour may seem harmful, but it actually benefits the environment in several ways. When they peck holes in trees, they create homes for other animals such as squirrels, bats, and insects. These holes also allow rainwater to enter the tree, preventing rot and disease.
By removing deadwood or decaying material from tree trunks they help keep the forest healthy by promoting new growth.
Moreover, the loud drumming noise made by woodpeckers can naturally repel insects and pests that may harm the tree.
| Read More: How To Attract Blue Jays- A Complete Guide
Woodpeckers primarily peck wood to find food. They have the unique ability to detect insects and larvae that are deep inside the wood, where other birds cannot reach. Additionally, woodpeckers create nest cavities by pecking holes in trees, which provide shelter and protection from predators for themselves and other birds.
Moreover, they play a significant role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Understanding and appreciating the unique qualities of woodpeckers can deepen our appreciation of the natural world.
FAQs
Are woodpeckers harmful to trees?
While woodpeckers do create holes in trees, they also provide many benefits to the environment and are not typically harmful to the overall health of the tree.
Can woodpeckers damage buildings?
While woodpeckers are primarily interested in pecking wood for food or nesting purposes, they may occasionally peck at wooden buildings or structures. However, this is not a common occurrence and can often be prevented by providing alternate nesting sites for woodpeckers.
Are all woodpeckers able to drum on trees?
Yes, all woodpeckers have the ability to drum on trees as a form of communication with other birds.
How fast can a woodpecker peck?
Woodpeckers can peck up to 20 times per second, with some species reaching speeds of over 15 miles per hour.
Do woodpeckers harm trees?
Woodpeckers do not harm healthy trees. They typically only peck on dead or dying trees where insects are more likely to be found.



